In the ever-evolving landscape of finance, cryptocurrency and smart contracts have emerged as transformative technologies, revolutionizing the way we interact with money and automate agreements. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or a curious newcomer, understanding the fundamentals of these concepts is crucial to navigating the exciting world of decentralized finance.
This article delves into the intricacies of cryptocurrency and smart contracts, shedding light on their inner workings and exploring the potential they hold for shaping the future of finance. From the basics of blockchain technology to the practical applications of smart contracts, we’ll unravel the key concepts that will empower you to make informed decisions in the exciting world of crypto.
Understanding the Basics of Smart Contracts
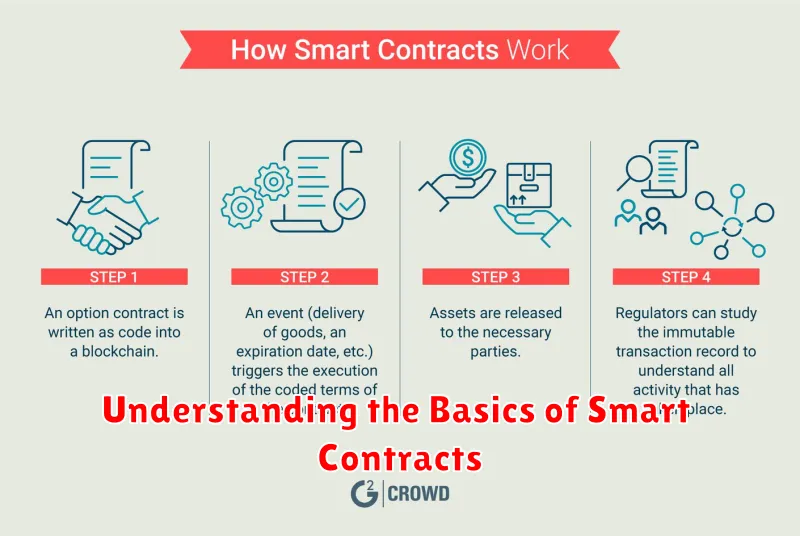
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements written in code and stored on a blockchain. They automate the execution of agreements, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of fraud. Essentially, a smart contract is a set of instructions that dictate how a transaction should be executed, including the conditions under which it can be executed.
Here’s what makes smart contracts unique:
- Transparency: All transactions and code are publicly viewable and verifiable on the blockchain.
- Immutability: Once deployed, the code of a smart contract cannot be changed, ensuring that the agreement remains as originally defined.
- Security: Cryptographic algorithms secure the blockchain, making it difficult for malicious actors to tamper with the code or data.
- Automation: Smart contracts automatically execute the agreed-upon terms when predetermined conditions are met, without requiring human intervention.
Smart contracts offer various benefits, including:
- Increased Efficiency: Automated processes streamline transactions, saving time and resources.
- Reduced Costs: Eliminating intermediaries lowers transaction fees and administrative costs.
- Enhanced Security: Immutable and transparent transactions minimize fraud and disputes.
- Improved Trust: Code-based agreements build trust between parties by enforcing pre-defined terms.
Some common applications of smart contracts include:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Facilitating lending, borrowing, and other financial services without intermediaries.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking goods and materials, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Digital Identity: Verifying identities and managing digital assets securely.
- Voting Systems: Ensuring secure and transparent elections.
Smart contracts are a powerful technology with the potential to revolutionize various industries. By understanding the basics of smart contracts, you can better grasp the potential impact of this transformative technology on the future.
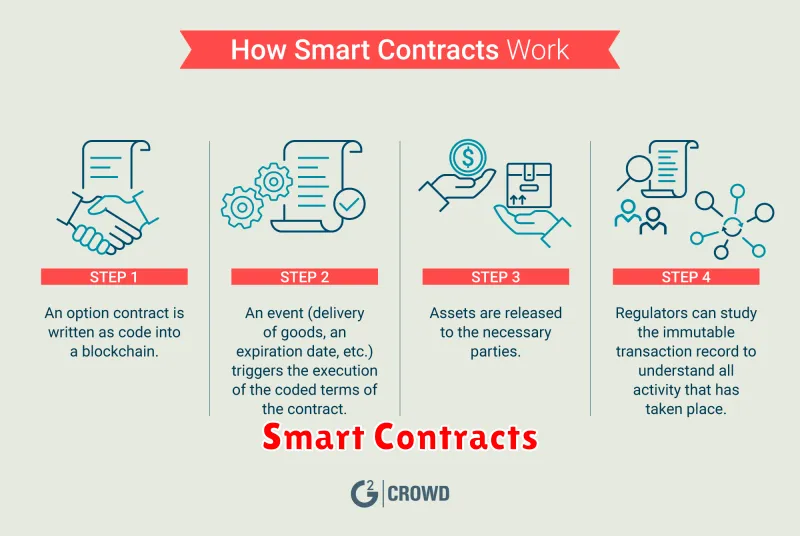
How Smart Contracts Work on the Blockchain
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements written in code and stored on a blockchain. They automate the execution of contractual terms, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of errors or fraud. When a specific condition is met, the smart contract automatically executes the predefined actions, ensuring transparency and security.
Here’s how smart contracts work on the blockchain:
- Code Deployment: The smart contract code is written in a programming language compatible with the blockchain platform and deployed onto the network.
- Triggering Events: When a specific event occurs, like a payment being made or a certain time being reached, the smart contract is triggered.
- Execution: The smart contract automatically executes the predefined actions, such as transferring assets, verifying data, or executing other predefined steps.
- Record Keeping: All transactions and actions taken by the smart contract are permanently recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and immutability.
Smart contracts leverage the decentralized and immutable nature of the blockchain to offer several benefits:
- Transparency: All actions are recorded on the blockchain, making it easy to audit and track contract execution.
- Security: The code is stored on a decentralized network, making it difficult to tamper with or alter.
- Automation: Smart contracts automate contractual terms, eliminating the need for intermediaries and minimizing human error.
- Efficiency: Smart contracts can execute transactions faster and more efficiently than traditional methods.
Smart contracts are a transformative technology with the potential to revolutionize how we conduct business and interact with each other. They are already being used in a wide range of applications, including supply chain management, voting systems, and decentralized finance (DeFi).
The Benefits of Using Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts stored on a blockchain. They automatically enforce the terms of an agreement between two or more parties. This eliminates the need for a third-party intermediary, such as a lawyer or bank, to oversee the transaction. This can save time, money, and effort for all parties involved.
One of the key benefits of using smart contracts is transparency. All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, which is a public ledger that anyone can access. This means that all parties can see the history of the contract and be sure that it has been executed properly.
Another benefit of smart contracts is security. Since the code is stored on the blockchain, it cannot be tampered with. This makes smart contracts much more secure than traditional contracts, which can be easily altered or forged.
Smart contracts can also be used to automate complex business processes. For example, a company could use a smart contract to automatically pay its suppliers when certain conditions are met. This can save time and reduce the risk of errors.
In addition, smart contracts can be used to create new types of applications and services. For example, a decentralized marketplace could be built using smart contracts to facilitate transactions between buyers and sellers. This could potentially lead to new business models and innovations.
Overall, smart contracts offer a number of advantages over traditional contracts. They are more transparent, secure, and efficient. This makes them an attractive option for businesses and individuals looking to streamline their operations and reduce costs.
Real-World Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements written in code and stored on a blockchain. They automate the execution of contractual terms, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of fraud. This technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries, and its real-world applications are becoming increasingly diverse.
One notable application is in the supply chain. Smart contracts can track goods from origin to destination, ensuring transparency and accountability. This can streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. For instance, companies can use smart contracts to automate payments upon delivery, eliminating the need for manual checks and reconciliation.
Another significant application is in the financial sector. Smart contracts can facilitate automated lending, insurance, and trading. For example, decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms leverage smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer lending and borrowing, eliminating the need for traditional financial institutions. This can make financial services more accessible and affordable.
Beyond finance, smart contracts have potential in healthcare. They can be used to manage medical records, automate insurance claims, and streamline patient care. For instance, a smart contract can ensure that medical data is only shared with authorized parties, enhancing patient privacy and security.
Furthermore, smart contracts can be used in the legal and governance sectors. They can automate legal processes, streamline voting systems, and ensure transparency in government operations. For example, a smart contract can automatically execute a will upon the death of the testator, eliminating the need for probate proceedings.
The possibilities for smart contracts are endless. As the technology evolves, we can expect to see even more innovative applications emerge in various industries. These applications have the potential to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and create new opportunities for businesses and individuals alike.
Challenges in Implementing Smart Contracts
While smart contracts offer numerous benefits, their implementation faces several challenges. One significant challenge is the security vulnerability of smart contracts. Once deployed on a blockchain, they are immutable, making any errors or vulnerabilities difficult to rectify. Auditing smart contracts is crucial to identify and address security risks before deployment.
Another challenge is the lack of standardized development practices. Different blockchain platforms have their own programming languages and development tools, leading to fragmentation and complexity. Establishing standardized practices would enhance interoperability and reduce development time.
Scalability is also a concern. Smart contract execution requires computational resources, and as the number of transactions increases, the network can become congested. Scalability solutions are essential to ensure efficient and timely execution of smart contracts.
Furthermore, legal and regulatory uncertainties surround smart contracts. The legal enforceability and jurisdiction of smart contracts are still under development, creating ambiguity for businesses and individuals.
Despite these challenges, research and development in the field are actively addressing these issues. As the technology matures, we can expect improvements in security, standardization, scalability, and legal clarity, paving the way for wider adoption of smart contracts.
The Future of Smart Contracts in Business

Smart contracts, self-executing agreements stored on a blockchain, have the potential to revolutionize business operations. By automating processes, reducing costs, and increasing transparency, they offer a new paradigm for conducting business.
One of the most significant impacts of smart contracts will be on supply chain management. By automating transactions and tracking goods in real-time, smart contracts can streamline logistics and reduce the risk of fraud. This can lead to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased trust among all parties involved.
Another area where smart contracts are poised to make a major impact is in finance. Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications powered by smart contracts are already enabling new ways to lend, borrow, and trade assets. These applications can offer lower costs, faster transactions, and greater accessibility than traditional financial institutions.
Beyond specific industries, smart contracts can also contribute to the broader business landscape by fostering trust and collaboration. By eliminating intermediaries and creating a verifiable record of agreements, smart contracts can foster a more transparent and efficient business ecosystem.
While the full potential of smart contracts is still unfolding, it’s clear that they have the potential to reshape the business world. As blockchain technology continues to mature and regulatory frameworks evolve, we can expect to see even wider adoption of smart contracts in the years to come.